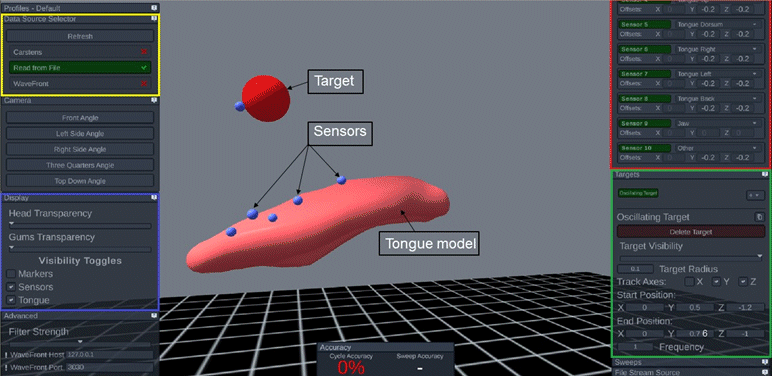
Visual feedback may assist in the acquisition of second language (L2) pronunciation skills. We are testing this premise by examining whether Optispeech provides superior training effects for L2 vowel and consonant articulation, compared with traditional pronunciation training methods.
For more information:
Mehta, S., & Katz, W. F. (2016). English listeners’ judgments of Japanese-accented English vowel productions: Relation to acoustic and kinematic characteristics. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 140(4), 3333-3333.
Berthier, M. L., & Moreno-Torres, I. (2016). Commentary: Visual Feedback of Tongue Movement for Novel Speech Sound Learning. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience; 10.
Katz, W. F., and Mehta, S. (2015). Visual feedback of tongue movement for novel speech sound learning. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, Vol. 9, Article 612.
Mehta, S., & Katz, W. F. (2015). Articulatory and acoustic correlates of English front vowel productions by native Japanese speakers. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 137(4), 2380-2380.
Mehta, S., Wang, J., & Katz W. (2014). Tense/lax discrimination in articulatory vowel space: Evidence from electromagnetic articulography, The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 135 (4), 2197.
